Matter
What is matter? Matter is any substance that has a mass and takes up space; everything!
Mass
What is mass? Mass is the measure of how many atoms are in a substance
How do you measure the mass of a solid? To determine the mass of a solid, a scale can be used. Solids can be measured easily by simply placing it on the scale.
How do you measure the mass of a gas and a liquid? For a liquid and a gas, a scale is still used but has extra steps. First, you must measure the mass of the container by itself. (Use the container that you are going to be putting the liquid / gas in.) Then measure the mass of the container with the liquid / gas in it. Find the difference between the two and it should give you the mass of the liquid / gas.
What units is mass in? The most common units are kilogram (kg) and gram (g).
Volume
What is volume? Volume is the space that a substance occupies.
How do you measure the volume of a liquid? Use a measuring container to measure the volume of a liquid.
How do you measure the volume of a regular solid? The formula for the volume of a regular solid is the length multiplied by the width multiplied by the height. (L x W x H)
How do you measure the volume of an irregular solid? The displacement method is a good way of finding the volume of an irregular solid. Fill up a container full of a certain amount of water, drop the irregular solid in the container of water and measure how much the water went up by (displaced) from its original amount. This will give you the volume for the irregular solid. Click here for the video of the displacement method.
What units is volume in? The most common units are millilitres (mL) and cm3.
Density
What is density? Density is the measure of mass per unit volume and measures how closely packed atoms are.
How do we measure density? The formula for measuring density is Mass / Volume. Using the methods above for mass and volume, the density of a substance can be found.
What units is density in? The most common units are kg/m3 , g/cm3 , g/mL
What is the density of water? 1.0 g/cm3
Something to remember: Objects sink when their density is greater than the density of water. Mass alone or volume alone are not enough to determine density. For example, a cruise ship has an enormous mass and a very large volume, but it is able to float because its density is less than the density of water.
Click here for an activity about density. Use the code CFHQCU to enter.
Solids, Liquids and Gases
Properties of a solid:
- Fixed shape (rigid)
- Fixed volume
- Not compressible
- Does not fill the container completely
Properties of a liquid:
- No fixed shape, fluid (can flow easily)
- Fixed volume
- Not compressible
- Does not fill the container completely (only its own volume)
Properties of a gas:
- No fixed shape, fluid (can flow easily)
- No fixed volume
- Compressible
- Fills the container completely
Particles:
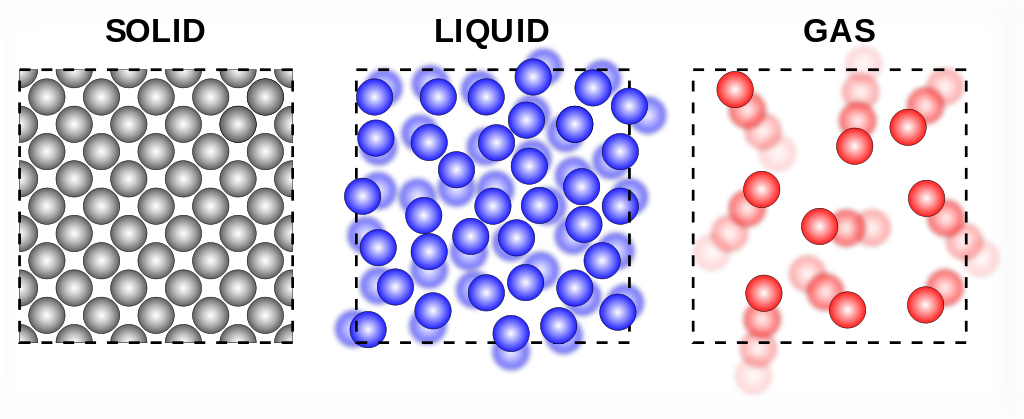
Particle Theory: As the temperature of a substance increases, the particles move faster. This means that they have more movement energy which is called kinetic energy. Kinetic energy can overcome the attraction between the particles when heated a lot.
Click here to enter an activity about particle theory. Use the code PGNAQI to enter.
Expansion and Contraction
What is Expansion? Expansion is when a material is heated. The particles vibrate more when they are hot so move further apart. This creates more space and the substance therefore expands.
What is Contraction? Contraction is the opposite of expansion. It is when a material is cooled. The particles vibrate less when they are cooled and therefore move closer together. This creates less space and the substance therefore contracts.
Click here for a useful worksheet on expansion and contraction.
Diffusion
What is diffusion?
Diffusion is the spread of a substance or the movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Click here for a useful video on diffusion that shows examples.
Changing State:
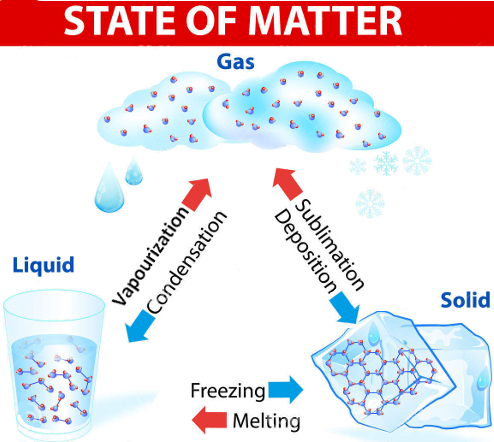
Note: it is easy to mix up vaporization, evaporation and boiling. So be careful! Click here to see a video on the difference between vaporization and evaporation.
Vaporization happens
Boiling Point and Melting Point
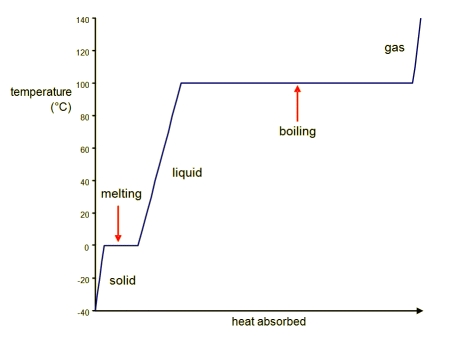
What is boiling point? The temperature at which boiling occurs for a liquid / substance.
What is the boiling point for water? 100 °C
What is melting point? The temperature at which melting occurs for a solid / substance.
What is the melting point for water? 0 °C
Heating Curve for Water