The Human Eye
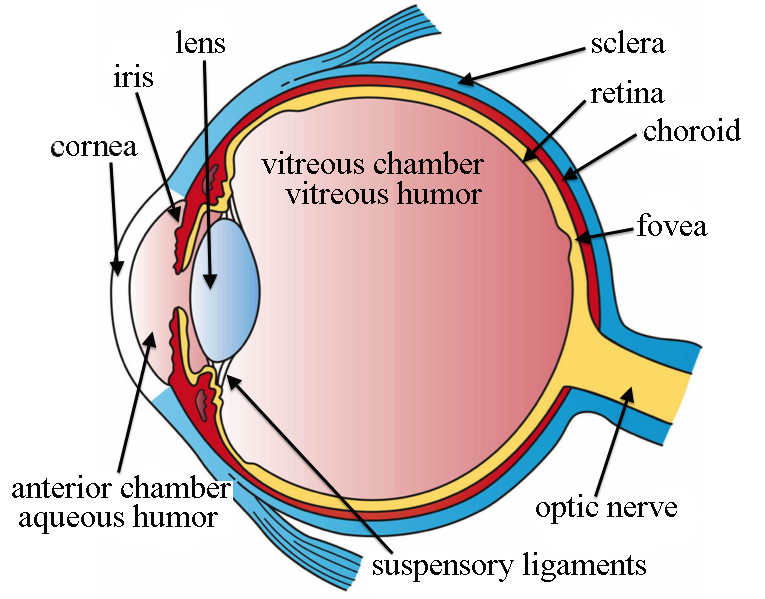
Parts of the Eye and Pathway of Light
- Cornea - clear, front part of the sclera
- Aqueous Humour - thinner than vitreous humour, liquid at front of the eye
- Pupil - small hole which changes size
- Lens - convex shape, allows light to focus on the retina, can change shape to focus
- Vitreous humour - thicker than aqueous humour, jelly-like substance at the back of the eye
- Retina - contains photoreceptors (more detail below), image formed in retina
- Optic nerve - connects to the brain, image interpreted in optic nerve
Not listed:
- Iris - coloured part of eye, contracts and relaxes to adjust the amount of light entering the eye
- Ciliary body - muscles that control the shape of the lens
- Sclera - white exterior of the eye
- Blindspot - the area where the optic nerve connects to the brain, does not have any light-sensitive cells, therefore cannot detect light
- Rods - allow you to see in black and white dim lighting, more sensitive to light
- Cones - allow you to see colour, less sensitive to light
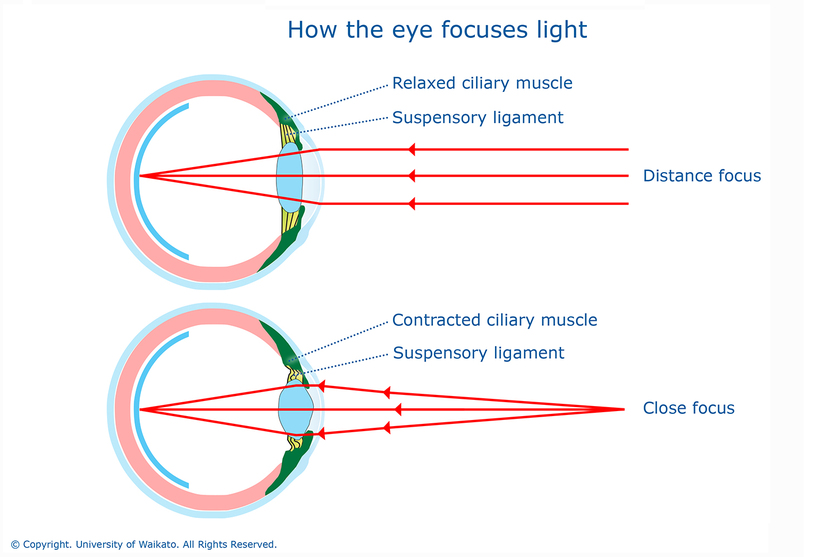
Accommodation
Accommodation is the change in optical power of the lens to maintain a clear image
- Optical power - the ability of a lens to focus light
- Focal point - the location where light focuses precisely on the retina
Glasses and Lens
The original lens in a human eye is a convex shape
Short sided people need concave lenses, the light focuses before the retina
Long sided people need convex lenses, the light focuses after the retina